Cooking and maturation
Applications
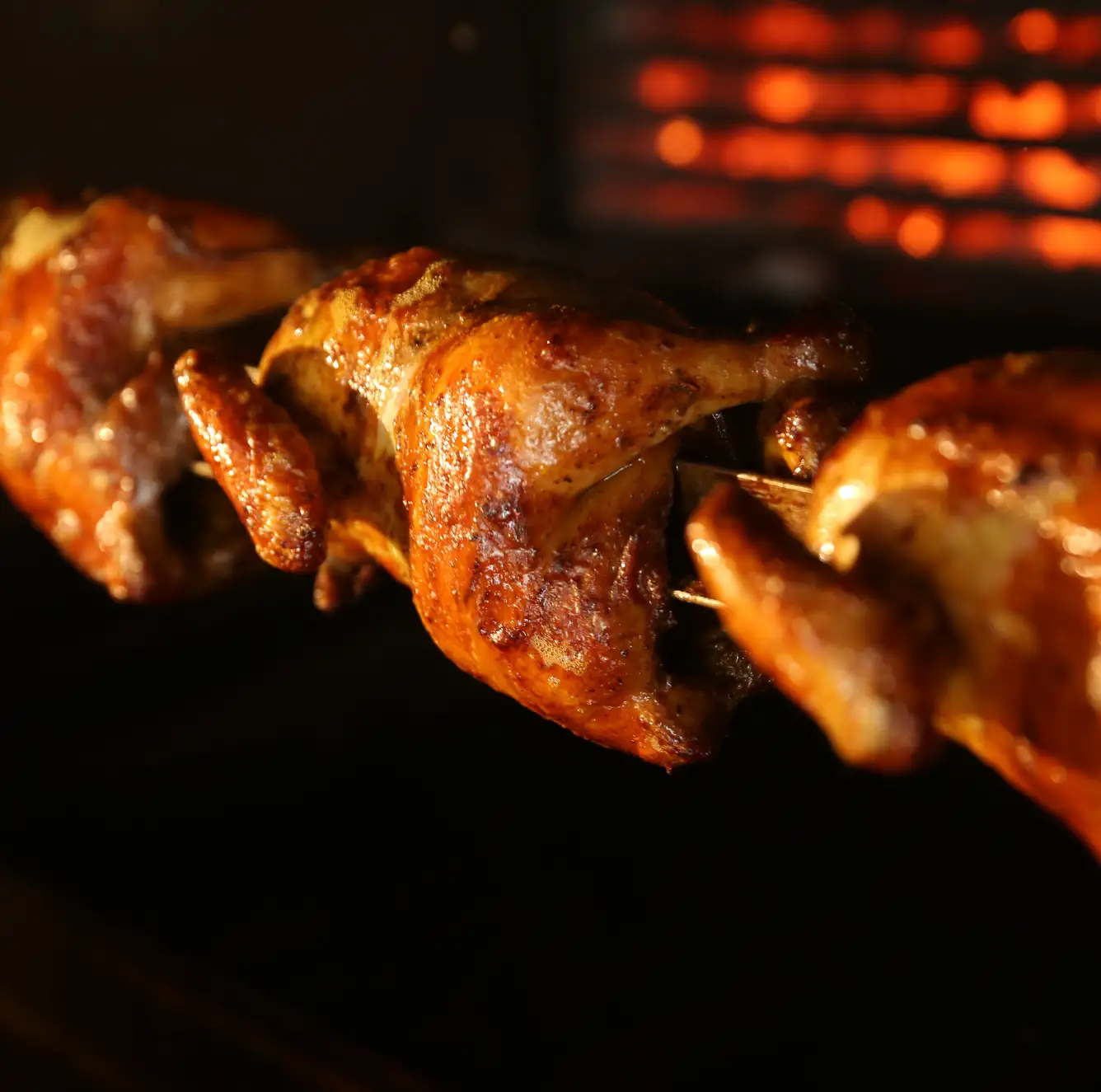

Infrared technology for cooking and maturing
Infrared technology is increasingly used in the food industry for processes like roasting, browning, crusting, braising, cooking, stabilizing, dehydrating, frying, melting and pasteurizing. It enables precise and efficient surface heating, allowing for optimal temperature control, reduced cooking times, and improved product quality.
By ensuring uniform heat distribution without direct contact, infrared technology helps preserve flavors, textures, and nutrients while enhancing efficiency. Whether in baking, pasteurization, or dehydration, it optimizes production, reduces energy consumption, and supports sustainable food processing.
Applications and benefits
Browning with IR tunnels enables only the surface of cooked dishes to be heated, without affecting the rest of the product, which is particularly useful for sheet pans and au gratin pizzas. In rotisseries, IR technology is used for aesthetic purposes, often combined with convection.
To stabilize packaged products after packaging, IR heats the surface through the packaging. For example, chocolate halves are heated several times before being filled and sealed. Infrared emitters also brown the toppings of instant meals without overcooking them, as in the case of pizzas that are pre-browned and then frozen for easy home cooking.
Optimization and practical use
Infrared heating can be adapted to avoid overcooking food surfaces by using a combination of IR and convection heating. Infrared emitters, whether electric or gas-powered, are used in a temperature range from 650 to 1200°C to prevent charring of products.
Electric IR emitters are popular for their precise control, speed and cleanliness. They also offer flexibility in producing the desired wavelengths for specific applications.
In conclusion, infrared technology offers significant advantages in terms of speed, energy efficiency and food quality. It has a wide range of applications in the browning, drying and cooking of food products, meeting the growing needs of the food industry.
Types of IR radiation
Infrared radiation is divided into three categories: NIR (0.75-1.4 μm), MIR (1.4-3 μm) and FIR (3-1000 μm). FIR is particularly advantageous for food processing, as it is well absorbed by most food components.
IR offers many advantages, including energy savings compared with hot-air ovens. IR waves pass through the air without heating it, and focus solely on the product, enabling rapid heating with a thermal inertia of 1 to 10 seconds. This improves processing times and increases production line speed, while requiring less floor space. IR-pasteurized foods can be packaged directly, and the technology enables precise control of processing conditions.

Our IR solutions for baking and curing

Restoration system
This type of system keeps food warm in canteens.
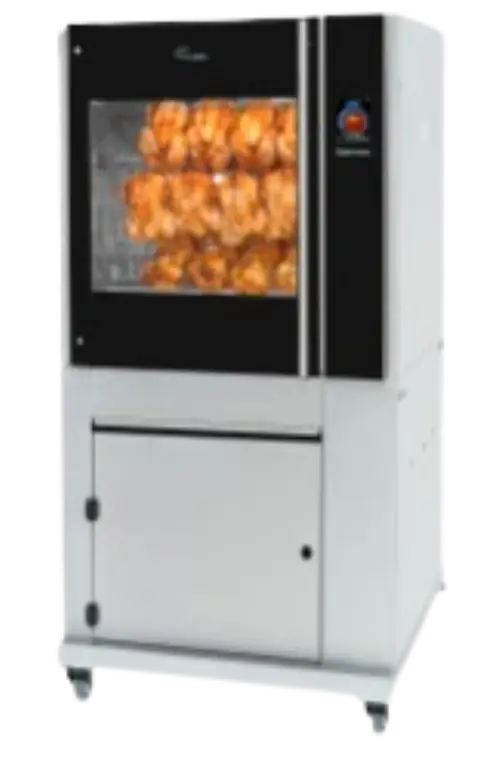

Rotisserie
Rotisseries can operate on IR.
Faceted lamp
This original type of IR lamp has been specially designed for pizza cooking.
