Bottle Blowing
Applications
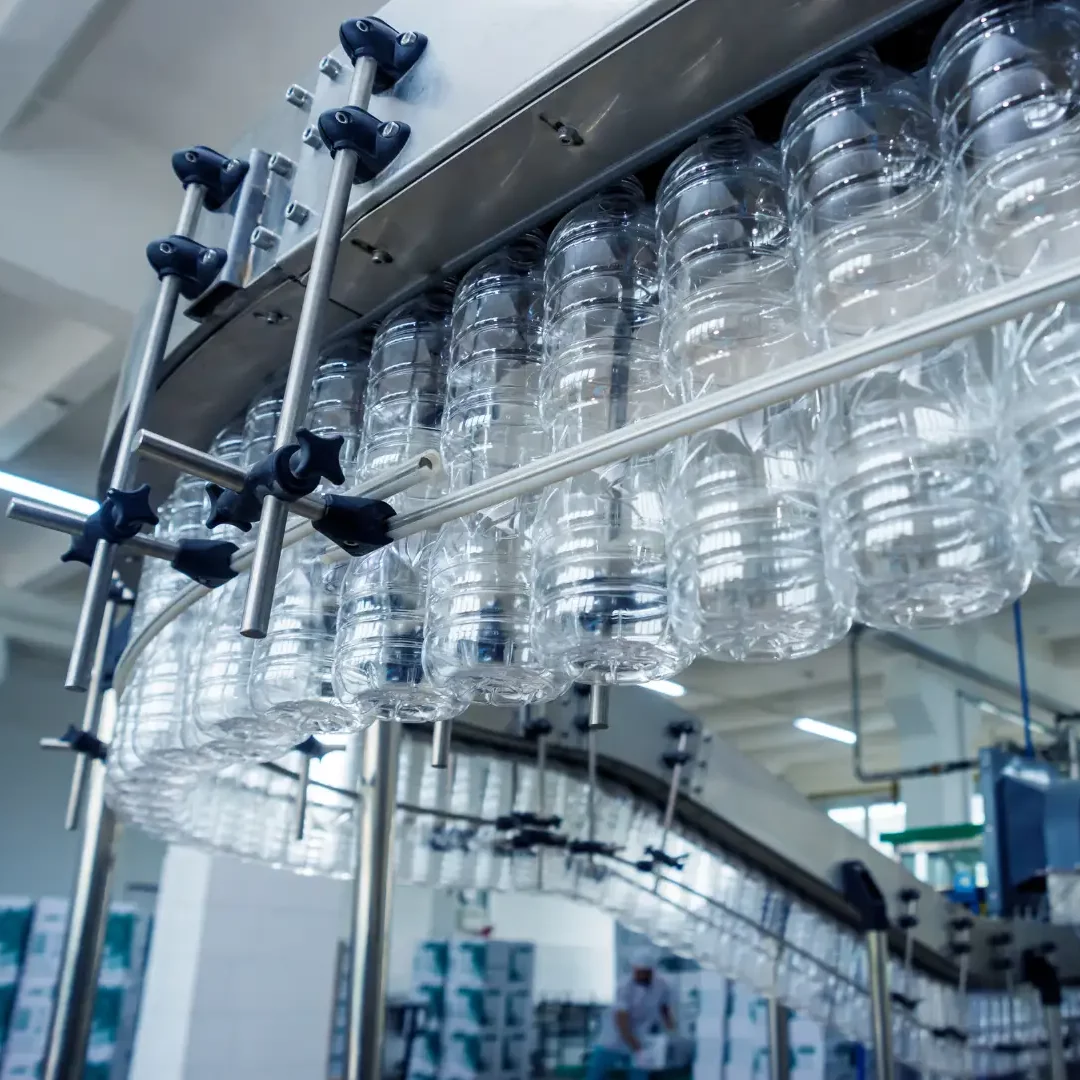

Infrared Technology in Bottle Blowing
Bottle Blowing, also known as the blow molding process, is an essential manufacturing method for plastic bottles and containers. In this process, a thermoplastic preform is heated, stretched, and inflated with compressed air into a mold to achieve the desired final shape. This technique is widely used for PET, PP, and PC bottles, which are commonly found in the packaging of beverages, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
A crucial factor in ensuring the quality of the final product is the precise heating of the preform. Our infrared technology enables uniform, efficient, and targeted heating, perfectly tailored to the requirements of the bottle blowing process. By using specific wavelengths, heat is applied exactly where it is needed – resulting in improved material distribution, shorter cycle times, and an energy-efficient production process.
Injection Stretch low Molding
Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) is a manufacturing process that combines the advantages of injection molding and blow molding to produce high-quality plastic bottles and containers. This method enhances efficiency, improves material properties, and reduces production costs. It is primarily used for PET, PP, and PC bottles in beverage, personal care, and pharmaceutical packaging.
The process begins with injecting molten plastic into a mold to form a preform, which is then reheated, stretched using a mechanical rod, and inflated with compressed air into the final shape. After cooling, the finished container is ejected, ensuring uniform wall thickness, high stability, and excellent transparency – ideal for modern packaging solutions.
The four main stages of bottle blowing:
Injection molding
Preform conditioning

Stretch blow molding

Ejection and cooling
Injection molding:
Preform production:
- Plastic resin (usually PET, PP or PC) is fed into the injection molding machine, where it is melted and injected into a preform mold. The preform mold is designed to create a partially formed product, called a “preform”. The preform has the finished neck and thread of the bottle, but with a thicker wall and smaller overall size.
Cooling:
- The preform is allowed to cool inside the mold, which helps it to solidify and retain its shape. The cooling time is important to ensure that the preform has the correct properties for the next stages of the process.
Preform conditioning:
Reheating:
- Cooled preforms are removed from the injection molding machine and transferred to the blow molding machine. Prior to the blow molding process, preforms are heated to a specific temperature range to ensure optimum material viscosity for stretch blow molding.
Temperature control:
- Temperature must be precisely controlled and evenly distributed throughout the preform to ensure consistent material properties and uniform bottle wall thickness during the blow molding process.
Dr Fischer is the worldwide leader of the this technology:
- Efficient heating is realized thanks to the combination of our LRP and a specific emitter wavelength.
Stretch blow molding:

Preform stretching:
- The heated preform is clamped inside the blow mold and a stretching rod is inserted into the preform. The drawing rod pushes the preform axially, causing it to elongate and the material walls to thin.
Blowing:
- High-pressure air is introduced into the preform, forcing it to expand against the walls of the blow mold. The combination of axial stretching and radial blow-molding ensures uniform material distribution, resulting in a strong, lightweight bottle with excellent transparency and barrier properties.
Ejection and cooling:

Cooling:
- After the blowing process, the newly formed bottle is left to cool inside the mold. Cooling time depends on factors such as bottle thickness, material type and mold temperature.
Ejection:
- Once the bottle has cooled and solidified, the blow mold opens and the finished product is ejected from the machine. The bottles are then inspected for quality and any excess material, such as burrs or tails, is removed.
Our customised solutions
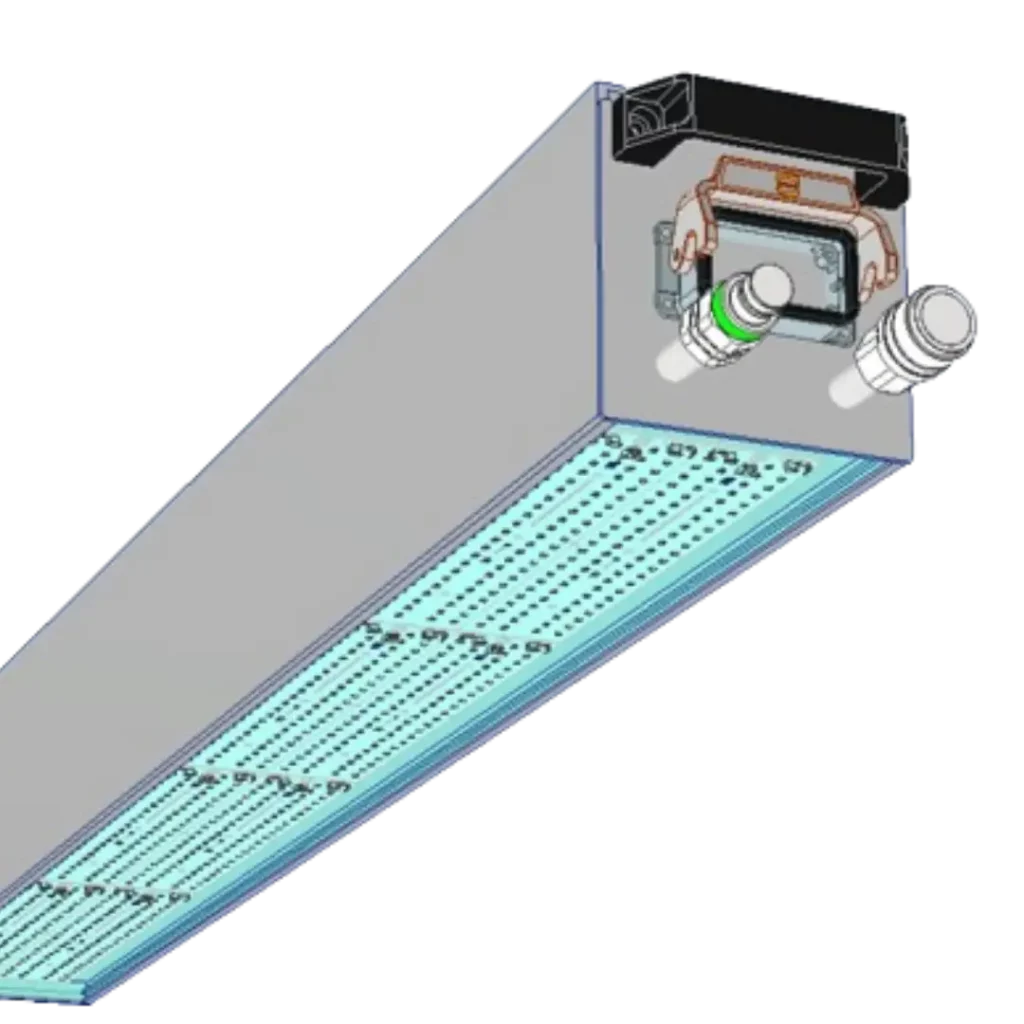
UV systems
UV LED (or lamp) systems for curing UV-curable adhesives
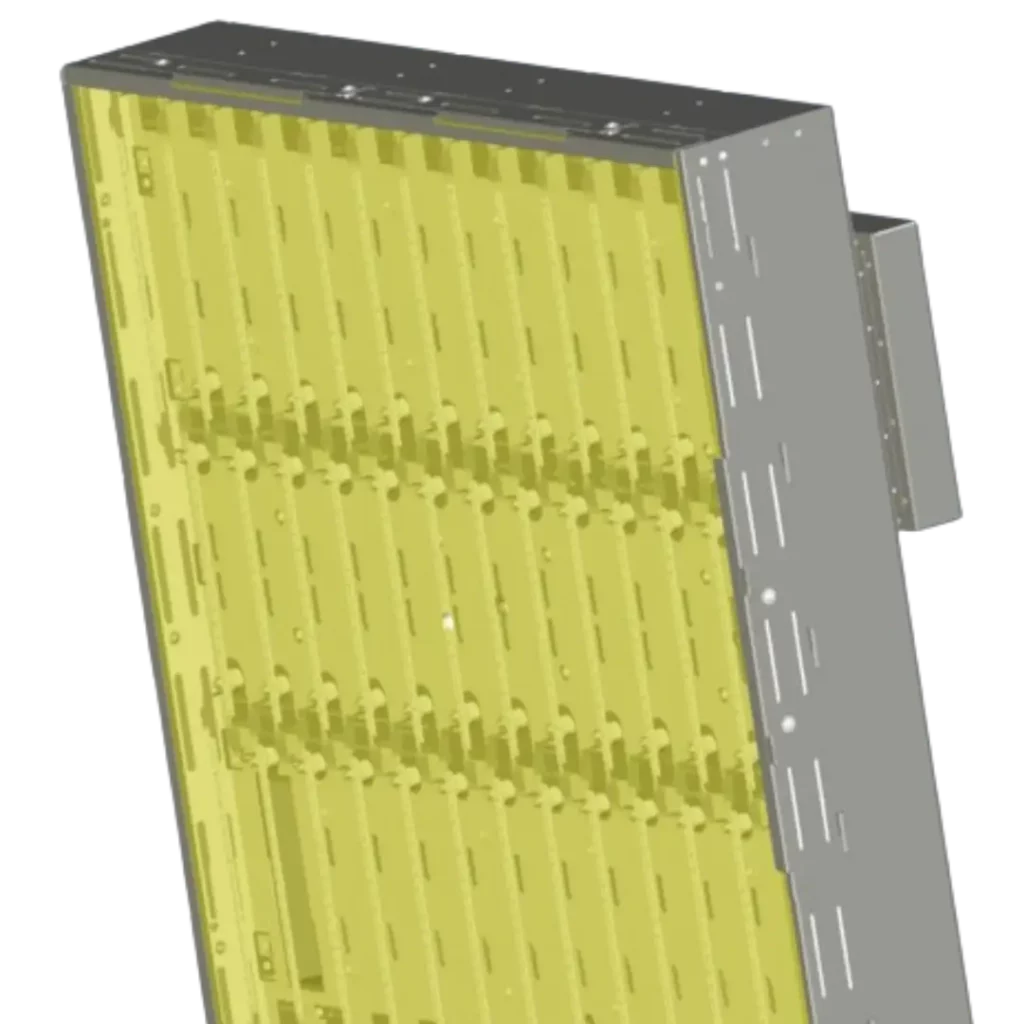
IR systems
IR systems for drying solvent-based adhesives
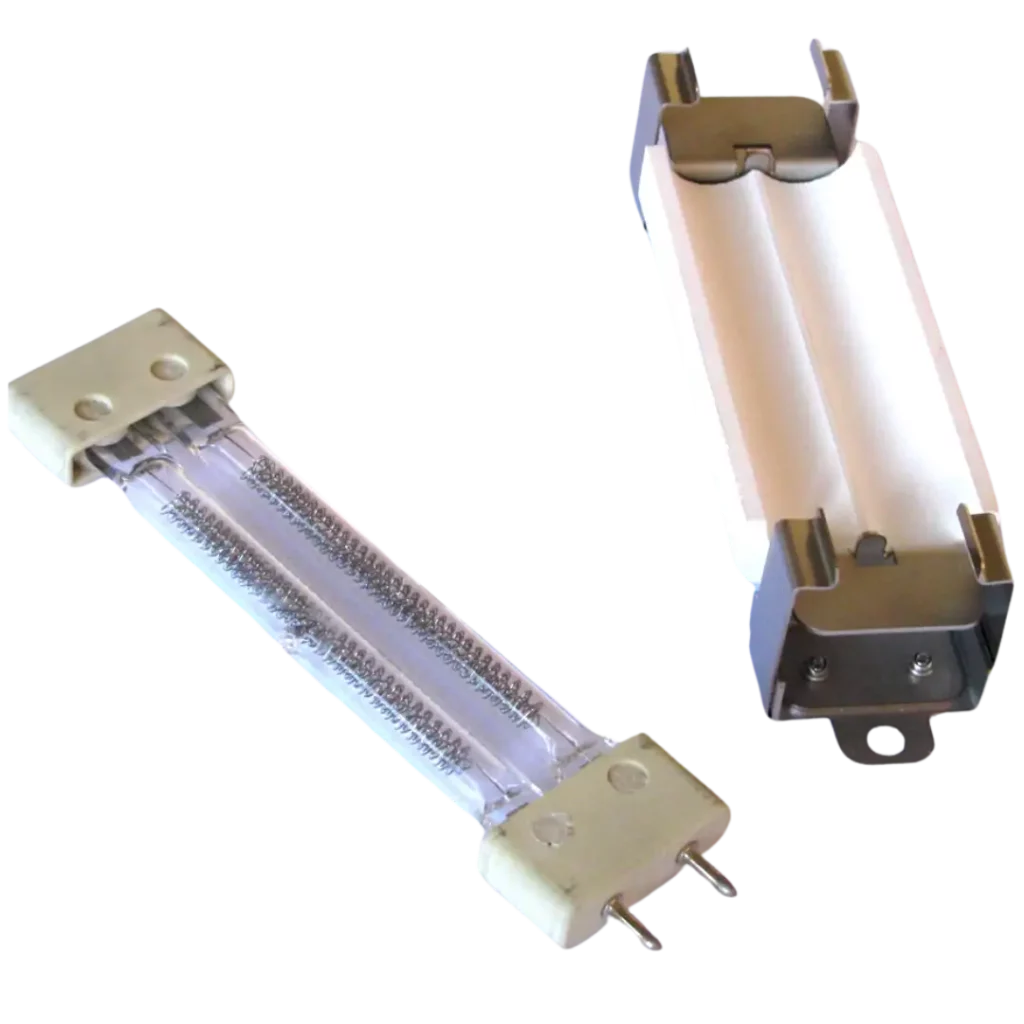

UV and IR lamps
UV and IR lamps adapted to different adhesive manufacturing processes
